From the 1930s to the early 1960s, the volume of mail — particularly business mail — grew significantly, and the need for a better system became apparent. On July 1, 1963, the USPS introduced the ZIP code. In 1967, ZIP codes became mandatory on all mail.
Making Sense of the Zip Code
What does the term “ZIP Code” mean?
A ZIP Code is a five-digit number that identifies a specific geographic mail delivery area. The acronym ZIP refers to Zone Improvement Plan, a plan implemented by the USPS in the early 1960’s to improve the sorting and delivery of mail.
How many ZIP Codes are there in the United States?
There are approximately 43,000 ZIP Codes in the United States. This number fluctuates from month to month, depending on the number of changes made.
How many changes are made to ZIP Codes monthly?
It varies from month to month and from year to year. Because of the schedule that the USPS uses to implement ZIP Code changes you may see a tendency for some months to consistently have more changes than others. ZIP Code changes are reported by the USPS in the form of addresses that have new or changed delivery information. While there are certainly many changes to ZIP Codes at the carrier route level many of these will have no impact on the 5-Digit ZIP Code boundary.
Where did ZIP Codes come from?
In the 19th and first half of the 20th century, mail was primarily transported by rail throughout the country and consisted mostly of personal correspondence. The growth of business and the use of mail as a sales and marketing tool rapidly changed the country and by 1963 business mail constituted 80% of the total volume. This was a direct result of the invention of the computer, which allowed companies to purchase and maintain large databases of customers and prospects. This eventually lead to an explosion of advertising, bills, statements etc. that were delivered by mail.
On July 1 in 1963 the Post Office implemented a new program aimed at taking advantage of new transportation systems now available (namely Interstate highways and air in addition to rail). Sectional Center Facilities (SCFs) were created, each of which was a central distribution point for 40-150 surrounding post offices.
A five-digit code was assigned to every address in the country. The first digit designated a general postal area (see map below), beginning in the northeast (0) to west coast (9). The next two digits referred to one of the Sectional Center Facilities accessible to common transportation networks. The final two digits designated individual post offices or postal delivery zones.
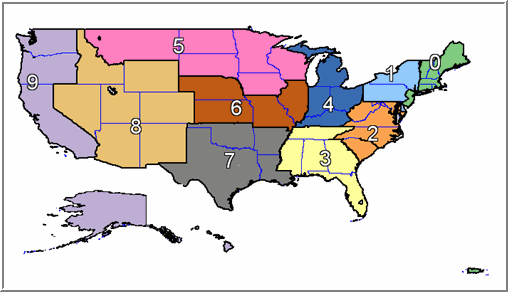
Postal Area Map ©Copyright TTG, Inc., 2010
What is a three-digit ZIP Code?
This refers to the first three digits of a 5-Digit ZIP Code. The first digit (0-9) designates the general area of the country with numbers starting lower in the east and increasing as you move west. For example: 0 covers Maine while 9 refers to California. The next two digits referred to one of the 450+ Sectional Center Facilities (SCFs) in the US.
Postal Areas (first digit of the 5-Digit ZIP Code)
| 0 | Connecticut (CT), Massachusetts (MA), Maine (ME), New Hampshire (NH), New Jersey (NJ), Puerto Rico (PR), Rhode Island (RI), Vermont (VT), Virgin Islands (VI) |
| 1 | Delaware (DE), New York (NY), Pennsylvania (PA) |
| 2 | District of Columbia (DC), Maryland (MD), North Carolina (NC), South Carolina (SC), Virginia (VA), West Virginia (WV) |
| 3 | Alabama (AL), Florida (FL), Georgia (GA), Mississippi (MS), Tennessee (TN) |
| 4 | Indiana (IN), Kentucky (KY), Michigan (MI), Ohio (OH) |
| 5 | Iowa (IA), Minnesota (MN), Montana (MT), North Dakota (ND), South Dakota (SD), Wisconsin (WI) |
| 6 | Illinois (IL), Kansas (KS), Missouri (MO), Nebraska (NE) |
| 7 | Arkansas (AR), Louisiana (LA), Oklahoma (OK), Texas (TX) |
| 8 | Arizona (AZ), Colorado (CO), Idaho (ID), New Mexico (NM), Nevada (NV), Utah (UT), Wyoming (WY) |
| 9 | Alaska (AK), American Samoa (AS), California (CA), Guam (GU), Hawaii (HI), Oregon (OR), Washington (WA) |
What is the difference between a 3-digit ZIP Code and an SCF?
An SCF (Sectional Center Facility) is a postal facility that serves as the distribution and processing center for post offices in a designated geographic area, which is defined by the first three digits of the ZIP Code of those offices. This facility may serve more than one 3-digit ZIP Code range.
3-digit codes refer to the first 3 digits of the 5-digit ZIP Code. For instance, the ZIP Code 55144 has a 3-digit of 551. Any ZIP Code starting with 551 would be grouped into this 3-digit area.
How many 3-digit ZIP Codes are there?
There are approximately 900 3-digit ZIP Codes in the United States.
Do other countries have ZIP Codes?
Other countries do have methods for distributing mail using various coding schemes (often referred to using the more generic term "Post Codes") they do not have "ZIP" Codes as defined by the USPS. For example, Canadians use a 6 digit coding scheme with a mix of characters and numbers called “FSALDU” where the FSA is similar to a US 5-Digit ZIP Code and the LDU is similar to a US ZIP+4.
Are there different kinds of ZIP Codes?
The USPS differentiates ZIP Codes as "standard" and "unique". A standard ZIP Code is one that is an established and usual ZIP Code, while a unique ZIP Code is one that only delivers to one specific large entity (such as a hospital, university or other unique delivery location).
What does “Unique” mean when referring to a ZIP Code?
A unique ZIP Code is a ZIP Code which includes only addresses within one specific large entity, for example a university, air force base or other large mail generating organization.
What is a ZIP+4 Code?
This refers to the 5-digit ZIP code plus a 4-digit add-on number which identifies a geographic segment within the 5-digit delivery area, such as a city block, office building, individual high-volume receiver of mail, or any other distinct mail unit. The purpose of +4 codes is to aid efficient mail sorting and delivery. Business mailers are the primary users of ZIP+4’s, because mailers who mail in bulk on the ZIP+4 or carrier route level can receive rate discounts.
Can ZIP Codes go across State, County, political jurisdictions and metro areas?
Yes, they can and do, however, this is not the norm. ZIP Codes rarely cross state lines but do more frequently cross county lines. You can see this yourself by viewing a ZIP code map. The reason for this is that ZIP Codes are service delivery areas and do not necessarily need to adhere to other geopolitical boundaries. For example, it may be more efficient to service a particular area from one post office even though it is in a different State or County.
How are boundaries for ZIP Codes defined?
The USPS does not define boundaries for ZIP Codes. Instead ZIP Codes represent groups of delivery points (addresses), designed for efficiency of delivery. In most cases ZIP Codes resemble spatial areas since they comprise contiguous streets and address ranges. However, this is not always the case. In rural areas, ZIP codes can be collections of roads (rural delivery routes) that in reality do not look much like a closed spatial area.
Are there areas of the nation that are not covered by a ZIP Code?
Yes, in sparsely populated rural areas where there is no mail delivery (deserts, mountains, lakes) ZIP codes are not defined. This creates unsightly "holes" in the ZIP Code boundary data. Some vendors have created polygons to fill in these holes and have given them their own arbitrary numerical designations - typically outside the range of numbers used by valid ZIP Codes.
What this means for Users of MissouriMVR
Instead of being tied down or forced to run multiple searches in multiple cities our users can run two or three-digit partial zip codes to narrow the search down to a specific localized area, county or zone. This allows more precise and accurate hitting of records, particularly with the more common names.
Users can use partial ZIP Code searching in combination with another full or partial identifier such as a year of birth, partial name, etc.